 Figure 1: A RAD7 connected using a Serial to Bluetooth adaptor will appear on one of the computer's serial ports.
Figure 1: A RAD7 connected using a Serial to Bluetooth adaptor will appear on one of the computer's serial ports.Long Distance Connectivity |
|
Under normal circumstances RAD7s and DRYSTIKs are directly connected to the computer running CAPTURE, using a null modem cable and a USB to serial adaptor, in the case of the RAD7, and a single USB cable in the case of the DRYSTIK. However when the device is in a dangerous or remote environment, it may be desirable to connect to it from a distance. This can be achieved via a Bluetooth adaptor or a local network. This section explains how to properly configure CAPTURE for long-distance communication. These instructions and the associated screenshots assume a RAD7 is being used, but the same approach applies to the DRYSTIK. Once CAPTURE has established a connection with a remote device, CAPTURE operations such as downloading and chart recording will proceed as they would normally. While Bluetooth-enabled devices may be detected by CAPTURE automatically, other long distance connection methods require clicking the Add Device button and using the Connection Method pop-up menu located at the top of CAPTURE's Main Window to choose the desired connection protocol. |
| Bluetooth Communications |
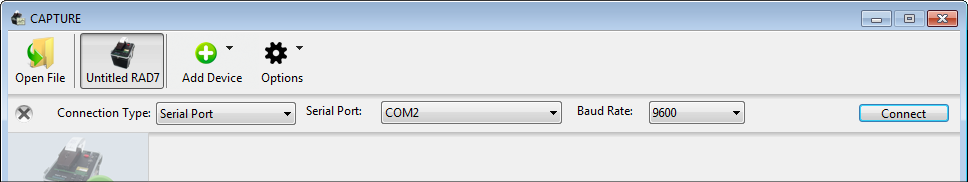
The simplest way to connect to a RAD7 remotely is through a Serial to Bluetooth adaptor attached to the RAD7's serial port. Since such adaptors create virtual COM ports in much the same way as a serial to USB adaptor, connecting to a Bluetooth-enabled RAD7 is as simple as clicking the Scan for RAD7s button in the CAPTURE window. DURRIDGE offers the SENA Parani SD1000 Serial to Bluetooth adaptor, preconfigured for use with the RAD7, making the connection process very straightforward. Other adaptor products may be used as well, however they must first be set to operate at the RAD7's specific baud rate. Third party adaptors must also be configured as "discoverable", and any command response behavior must be disabled to avoid corrupting the RAD7 with garbage data. The procedure for completing this configuration will vary by adaptor. DURRIDGE provides detailed instructions on using the SENA Parani SD1000 Serial to Bluetooth adaptor with the RAD7. Please see the RAD7 Bluetooth Connectivity guide for details. |
 Figure 1: A RAD7 connected using a Serial to Bluetooth adaptor will appear on one of the computer's serial ports.
Figure 1: A RAD7 connected using a Serial to Bluetooth adaptor will appear on one of the computer's serial ports. |
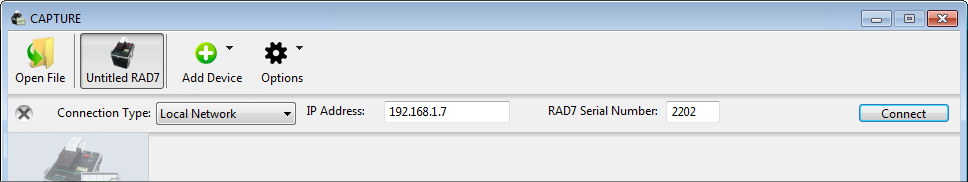 Figure 2: Connecting to a RAD7 using a local network.
Figure 2: Connecting to a RAD7 using a local network. |
|
On the computer that is attached directly to the RAD7 or DRYSTIK, enter the Relay RAD7 Commands or Relay DRYSTIK Commands panel, as shown in Figure 3. Click the Listen button to prepare to receive remote commands. This will allow any commands received by the computer to be passed on to the device, where they will be acted upon. Once CAPTURE is listening for incoming commands, the Listen button will change to Stop. |
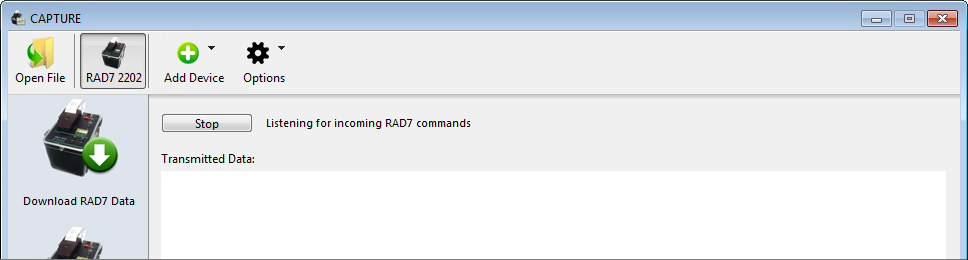 Figure 3: Relaying RAD7 commands.
Figure 3: Relaying RAD7 commands. |